Start a new topic and get direct answers from the Expert Advice Community.
CREATE NEW TOPIC +Search results
11275 results
Guest
Guest
Create New Topic As guest or Sign in
Assign topic to the user

-
ISO 27001 Certificate Renewal
Since your previous certification has expired, you need to go through all the certification processes again (i.e., first a certification audit, followed by surveillance audits).
Compared to ISO 27001:2005, ISO 27001:2013 has significant differences only in Annex A (security controls), so you do not need to consider a full fresh implementation (i.e., documents related to main clauses from sections 4 to 10 will need only some adjustments).
For further information, see:
- ISO 27001 implementation steps https://advisera.com/27001academy/knowledgebase/iso-27001-implementation-checklist/
- How to make a transition from ISO 27001:2005 revision to 2013 revision https://advisera.com/27001academy/knowledgebase/how-to-make-a-transition-from-iso-27001-2005-revision-to-2013-revision/ -
Questions around templates - policies vs procedures
Please note that ISO 27001 does not prescribe how police and procedures need to be documented, so organizations are free to document them as best fit their needs (i.e., separated, or merged documents).
For large organizations, policies define the general rules for activities to be performed (what needs to be done), while procedures define specific steps to perform them (how to do).
For example, a Backup Policy can define that those users need to periodically update local data to corporate storage, and you can have specific procedures on how to do that considering different devices, operational software, or work sites.
For small organizations, you can have all this information in a single document, to reduce administrative effort.
These articles will provide you a further explanation about developing documents:
- 8 criteria to decide which ISO 27001 policies and procedures to write https://advisera.com/27001academy/blog/2014/07/28/8-criteria-to-decide-which-iso-27001-policies-and-procedures-to-write/
- How detailed should the ISO 27001 documents be? https://advisera.com/27001academy/blog/2014/09/22/detailed-iso-27001-documents/
-
Most efficient steps in regulatory pathway to introduce class III implantable device
Please consider the following steps:
Establish QMS - compile a dossier of pre-clinical evidence - seek regulator approval for phase I safety trial - prepare the technical documentation - CE mark product and ISO13485 certification (last two steps goes together). -
PHA risk evaluation
1. In the document ISO 13485 & MDR Integrated Documentation Toolkit – does MDR 2017/745 correspond to all 2017/746 requirements?
Our toolkit corresponds to most of the MDR requirements for the Quality Management system. We are doing right now on some more documents to be completely in compliance with Article 10 and you will be informed about it as soon as it is published.2. I need to create a PHA risk evaluation analysis for my medical device (photometer). I do not think that in this toolkit there is a template for PHA risk evaluation for an electrical device. Is it possible to request this document from you or to buy it separately?
No, we do not have a template for the PHA. We considered that our risk traceability matrix is best that describe the requirements from the ISO 14971:2019. -
Training and ISO 27001 implementation
Your assumption is correct. Required information security training and awareness activities, and which personnel is required to attend them, are mapped in the Training Module, but please note that this tracking is not done automatically. You need to define manually these activities, according to the competencies you identify you need to have.
From a standard point of view, the information included in the Training module is sufficient for certification purposes. In case you already have any other solution implemented for tracking training in your company you may include the information about information security training and awareness on it.
-
Privacy policy on my homepage
A privacy policy is usually an internal document, used to establish how personal data processing operations are handled by the organization, generic controls for the protection of personal data, and escalation paths. A privacy notice or privacy statement is something you communicate to data subjects whose data you process, as part of your transparency obligation.
In a privacy notice, you need to be very precise regarding the processing of personal data that you, as a data controller, are doing. Transparency is one of GDPR’s most important principles, as it is required in Article 5.1.a. So you need to determine whether you are using Google Fonts and then you must provide all details, including any personal data transfers to the US and the safeguards you are using to protect personal data.
Please find more details at these links:
- Article 5 GDPR - Principles relating to processing of personal data: https://advisera.com/gdpr/principles-relating-to-processing-of-personal-data/
- Article 46 GDPR - Transfers subject to appropriate safeguards: https://advisera.com/gdpr/transfers-subject-to-appropriate-safeguards/
- Everything you need to know about the GDPR Privacy Notice: https://advisera.com/articles/gdpr-privacy-notice-6-key-elements-to-include/
-
Questions about ISO 27001 controls in Conformio
1. We have a question about this Time synchronization control - the control in Conformio says to use accurate time clocks and synchronize them automatically. We have a system in place to synchronize clocks and our laptops that the employees use are also synchronized via google services. We would like to understand if we should write a policy about this and what can we expect during the audit? Will the auditor ask to see how we do this for all clocks and laptops or will he ask for a random one? Would this also be applicable to tablets? This is the task I am referring to
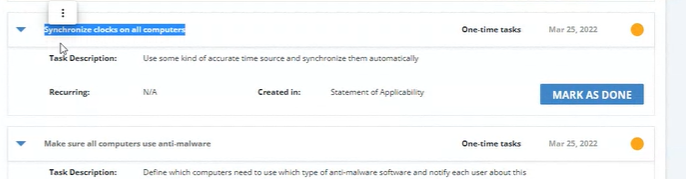 (control A12.4.4)
(control A12.4.4)Answer: ISO 27001 does not require control A.12.4.4 - Clock synchronization to be documented, so you can simply add the information on how it is implemented in the Statement of Applicability, by accessing it through the Statement of Applicability module.
Regarding activities during the audit, the auditor will want to see how you planned to implement this control (he can find this information in the SoA as we suggested) and choose some random devices to verify the implementation. All devices that have access to the information you want to protect (as defined in the ISMS scope) need to be covered by this control if it is applicable, including tablets.
2. We have similar questions around the task "Make sure all computers use anti-malware" related to control A 12.2.1 - what would the auditor check in relation to this and do we need a written policy on how we handle this in our organization?
Answer: Control A.12.2.1 - Controls against malware also do not need to be documented, but as a commonly adopted practice, in case this control is defined as applicable, its implementation is documented in the IT Security Policy.
Regarding activities during the audit, the auditor will check if what was defined in the IT Security Policy is implemented.
For further information, see:
- 8 criteria to decide which ISO 27001 policies and procedures to write https://advisera.com/27001academy/blog/2014/07/28/8-criteria-to-decide-which-iso-27001-policies-and-procedures-to-write/
- How to structure the documents for ISO 27001 Annex A controls https://advisera.com/27001academy/blog/2014/11/03/how-to-structure-the-documents-for-iso-27001-annex-a-controls/
- Which questions will the ISO 27001 certification auditor ask? https://advisera.com/27001academy/blog/2015/07/20/which-questions-will-the-iso-27001-certification-auditor-ask/
3. Also, the standard uses the word elements to be considered and they give 10 recommendations? Are these recommendations or do we need do everything that is listed?Answer: From the extra information you’ve sent, I identified that you are referring to ISO 27002 in this question.
Considering that, please note that ISO 27002 is not mandatory for implementing ISO 27001. ISO 27002 is usually used by consultants who want to learn more about the standard.
For example, the implementation of whitelists or blacklists (recommendations b and c for control A.12.2.1 – Controls against malware) are necessary only in case you have relevant risks that can be treated by implementing such lists, or if you have to be compliant with a law, regulation or contract that demands the implementation of such lists.
-
Complying with IATF
Generally, MTTR, MTBF, break down percentage, line stop hours or minutes, etc. are followed as maintenance process indicators and targets.
In general, the parts of the IATF 16949:2016 standard related to the maintenance process; Articles 8.5.1.4, 8.5.1.5, 8.5.1.6,7.1.4.1, and 6.1.2.3.
These topics are plant, production, measurement, etc. periodic maintenance of equipment, predictive maintenance, preventive maintenance, TPM, break down maintenance, cleanliness, repair and contingency actions, and plans to prevent the production and/or delivery to the customer.
In particular, I recommend that you examine these 3 items closely.
-
Is Security Awareness training complaint enough for ISO 27001 audit?
Please note that the awareness training included with your Conformio plan covers the most common topics related to general employees training and awareness, but to be sure if it is enough for auditing purposes you need to verify the results of your risk assessment and applicable legal requirements (i.e., laws, regulations, and contracts) to check if no specific additional training is required.
For further information, see:
- How to perform training & awareness for ISO 27001 and ISO 22301 https://advisera.com/27001academy/blog/2014/05/19/how-to-perform-training-awareness-for-iso-27001-and-iso-22301/
-
Best laboratory practices
General best practices in laboratories involve establishing a quality management system with criteria for a safe working environment, efficient processes and valid results. The specifics depend on the type of laboratory. For example, for non-clinical safety studies, the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) sets out Principles of Good Laboratory Practice (GLP) to ensure the quality and integrity of test data related to non-clinical safety studies.
ISO 17025 is the basis of the quality management system for testing and calibration laboratories. Then depending on the sector and risk, practices for safety and environmental protection could include certification to other ISO or other international standards, for example, ISO 14001.
For more information to meet ISO 17025 requirements, see the complimentary white paper (PDF) Clause-by-clause explanation of ISO 17025:2017 available at https://info.advisera.com/17025academy/free-download/clause-by-clause-explanation-of-iso-17025/ and the ISO 17025 Toolkit at https://advisera.com/17025academy/iso-17025-documentation-toolkit/
